Respiration in Organisms
What is Respiration?
- A process in living organisms involving the production of energy, typically with the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide, is called respiration.

- When the breakdown of food, i.e. glucose, occurs in the presence of oxygen, it is called aerobic respiration.

- When the breakdown of food, i.e. glucose, occurs in the absence of oxygen, it is called anaerobic respiration.
Anaerobic Respiration in Muscles
We (human beings) normally obtain energy by aerobic respiration. But under certain conditions (when extra energy is needed), anaerobic respiration can take place in our muscles for a short time. When the oxygen gets used up faster in our muscle cells than can be supplied by the blood, then a temporary deficiency of oxygen occurs in the muscle cells.
For example: When we do a heavy physical exercise (fast running, cycling or weightlifting, etc.), our muscles need a lot of energy. To produce more energy, our muscles need more oxygen. But the supply of oxygen through blood-is limited and hence insufficient. Under these conditions, anaerobic respiration takes place in the muscle cells (without oxygen) to produce extra energy and fulfil the demand for more energy.
When anaerobic respiration takes place in our muscle cells in the absence of oxygen, then glucose (food) breaks down partially to form lactic acid and releases some energy. This extra energy helps us in doing hard physical exercise.
After a heavy physical exercise (very fast running, etc.), we sometimes get muscle cramps (Painful contractions of muscles are called cramps) . During heavy exercise, some of our muscles respire anaerobically. The anaerobic respiration by muscles brings about partial breakdown of glucose (food) to form lactic acid. This lactic acid accumulates in the muscles. Thus, muscle cramps occur due to the accumulation of lactic acid in muscles when the muscles respire anaerobically (without oxygen) while doing hard physical exercise.
We can get relief from cramps in muscles caused by heavy exercise by taking a hot water bath or a massage. Hot water bath (or massage) improves the circulation of blood in the muscles. Due to improves the supply of oxygen to the muscles increases. This oxygen breaks down lactic acid accumulated in muscles into carbon dioxide and water, and hence gives us relief from cramps.
Similarity between aerobic and anaerobic respiration
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| Energy is produced by breakdown of food like glucose. | In this also energy is produced by breakdown of food like glucose. |
| It take place in the cells of the organism. | It also takes place in the cells of the organism. |
Difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| It takes place in the presence of oxygen. | It takes place in the absence of oxygen. |
| Complete breakdown of food occurs in this. | Partial breakdown of food occurs in this. |
| The end products are Carbon dioxide, water and energy. | The end products are alcohol and carbon dioxide or lactic acid. |
| It produces large amount of energy. | It produces less amount of energy. |
Respiration in Humans
- The process of taking in oxygen rich air into the body is called inhalation, and giving out of air rich in carbon dioxide is known as exhalation.
- The process of inhalation and exhalation together is called breathing.
Breathing Rate
The number of times person breathes in one minute is called breathing rate.
The average breathing rate in an adult human being at rest is 15-18 times per minute. Women breathe slightly faster than men.
The breathing rate of a person changes according to the oxygen requirements of the body.
1. The breathing rate of a person is the slowest when he is sleeping because minimum energy is required by the body during sleep which can be provided by a slow rate of breathing.
2. The breathing rate of a person increases with increased physical activity (like exercise, running, weightlifting, etc.). When the breathing rate increases, greater amount of air goes into the lungs. With more air going into the lungs, the blood can absorb oxygen at a faster rate. Thus, faster breathing supplies more oxygen to the body cells for producing more energy (by the rapid breakdown of food) needed for doing heavy physical exercise, etc.
When we run , we also take deep breaths so as to inhale more air (and get more oxygen) for the speedy release of energy from food. Athlete breathes faster and deeper than usual even after finishing a race. This is because during the race, the leg muscles of athlete have produced extra energy by doing anaerobic respiration (without using oxygen). By breathing faster and deeper, the athlete is giving back oxygen to the muscles which it could not give earlier at the time of running.
We feel hungry after doing a heavy physical exercise . This is because to provide extra energy for doing heavy physical exercise, the food has broken down very rapidly (by faster breathing) and made us feel hungry.
Children breathe about 20 to 30 times per minute
Mechanism of Breathing
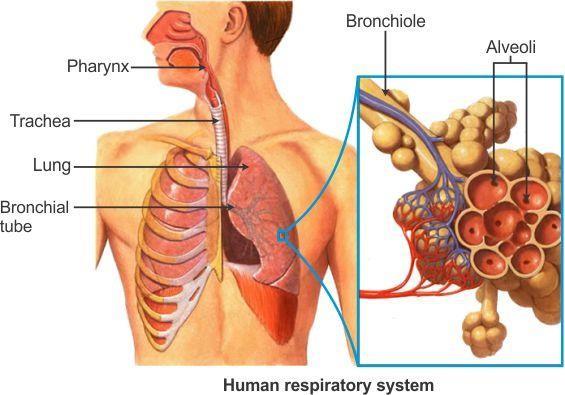
- Air inhaled through the nostrils passes into the nasal cavity and reaches the lungs through the windpipe.
- The windpipe, also known as trachea, branches into two smaller tubes called bronchi at its lower end; the two bronchi are connected to the two lungs.
- Lungs are present within the chest cavity which is surrounded by ribs on the sides.
- Each bronchus is further divided into still smaller tubes called bronchioles which have air-sacs at their ends called alveoli.
- Exchange of respiratory gases between air and blood occurs in the alveoli.
Activity: Mechanism of Breathing
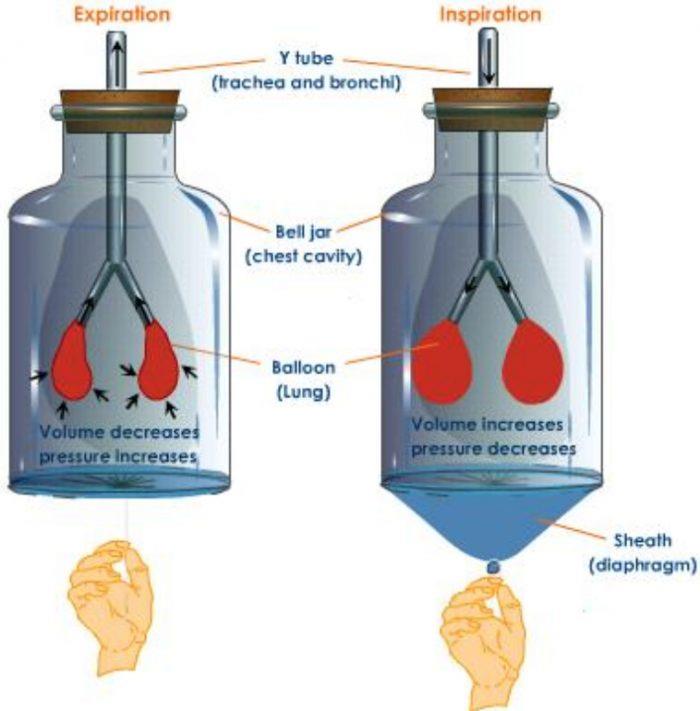
A big bell jar is taken (The bell jar is a glass jar whose bottom is open). A glass tube branching into two smaller tubes at its lower end is fitted in the mouth of the bell jar with the help of a cork. Two balloons are tied at the two ends of the tube. A thin rubber sheet is tied around the open bottom of the bell jar. In this apparatus, the space inside the bell jar represents the chest cavity, the balloons represent the lungs whereas the rubber sheet represents the diaphragm.
- To show the process of breathing in air, we pull the rubber sheet downwards. In this case, the space in the bell jar increases, lowering the air pressure inside the bell jar. The air from outside rushes in through the tube into balloons due to which the balloons get inflated (their size increases).This shows the action of diaphragm during inhaling of air.
- To show the process of breathing out of air, we release the rubber sheet. In this case, the space in the bell jar decreases. The air from inside the balloons goes out through the tube due to which the balloons get deflated (their size decreases). This shows the action of diaphragm during exhaling of air.
When the diaphragm moves downward during inhaling, the lungs get filled with air. But when the diaphragm moves upward during exhaling, then the air is forced to go out of the lungs.
Air Which We Breathe During Respiration
The air which we breathe in from the atmosphere is called inhaled air and the air which we breathe out (from our lungs through nose or mouth) is called exhaled air.
The only difference in the inhaled air and exhaled air is that they contain different proportions of oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapour.
- The Case of Oxygen: The air which we inhale contains a higher proportion of oxygen. Some of the oxygen of inhaled air is used up in breaking down glucose food during respiration. So, the exhaled air which comes out after the process of respiration contains a lower proportion of oxygen. Thus, exhaled air contains less oxygen than inhaled air.
- The Case of Carbon Dioxide: The air which we inhale contains a lower proportion of carbon dioxide. Now, during respiration when oxygen breaks down glucose food, then some carbon dioxide is produced. Thus, exhaled air contains more carbon dioxide than inhaled air.
- The Case of Water Vapour: The air which we inhale contains only a little of water vapour. When glucose (food) is broken down by oxygen during respiration, then water is also produced (along with carbon dioxide). So, the exhaled air contains a lot more water vapour than inhaled air.
If we exhale air on a mirror through our mouth, then a patch of moisture is formed on the mirror surface. This is because the exhaled air coming from our mouth contains a lot of water vapour. This water vapour condenses on the mirror surface to form tiny droplets of water which appear as a patch of moisture.
Activity: Carbon dioxide is produced during respiration
The apparatus consists of two boiling tubes and fitted with two-holed corks. The boiling tubes are connected through a special type of glass tube . The left arm of glass tube is short which goes in the boiling tube . The right arm of glass tube is long and dips in lime water in boiling tube.The boiling tube has another bent glass tube whose longer side dips in lime-water contained in it. The boiling tube has also another short, bent tube E in it which does not dip in lime-water.
We put the top end of the tube in mouth and breathe in and ‘breathe out gently.When we breathe in, then the inhaled air (fresh air) enters the glass tube and passes through the lime-water in boiling tube . And when we breathe out, then the exhaled air (coming from our lungs) passes through the lime-water in boiling tube . We continue to breathe in and breathe out for about five minutes.
We will find that the lime-water in boiling tube (in which inhaled air is passed) turns milky only slightly but the lime-water in boiling tube (in which exhaled air is passed) turns milky appreciably. This shows that less carbon dioxide is present in inhaled air but much more carbon dioxide is present in exhaled air.
Respiration in Animals
- Animals such as insects respire through spiracles through which air enters and is transported to every cell of the body.
- Fishes breathe through gills. They take in the oxygen dissolved in water.
- Earthworms breathe through the skin. They absorb oxygen from the air which is then transported to all the cells in the body via blood.
- Frogs can breathe through their lungs as well as their moist skin.
Respiration in Plants
- Plants breathe in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide.
- In plant cells, glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water in the presence of oxygen.
- The exchange of gases occurs by means of tiny openings called stomata present on the lower surface of the leaves.
- Oxygen enters the leaf through the stomata and reaches all the cells by diffusion. Carbon dioxide produced also diffuses out through the same stomata.


