Reproduction in Plants
- The production of new individuals from parents is known as reproduction.
- Plants reproduce sexually as well as asexually.
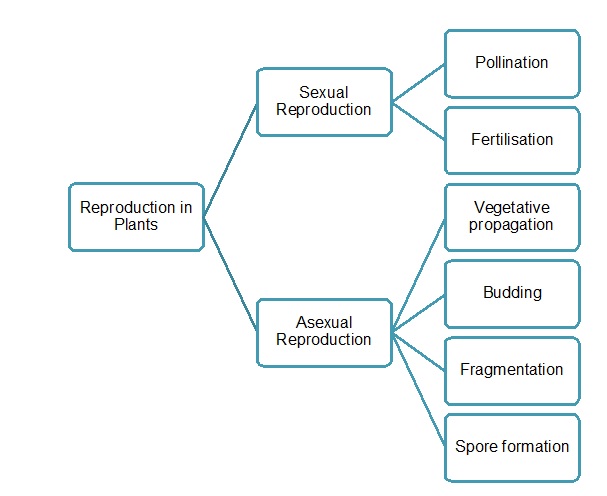
Asexual Reproduction
- In asexual reproduction, new plants are obtained without the production of seeds or spores.
Vegetative Propagation
- In this type of reproduction, new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds.
- Since these parts are known as vegetative parts of a plant, this type of reproduction is termed as vegetative propagation.
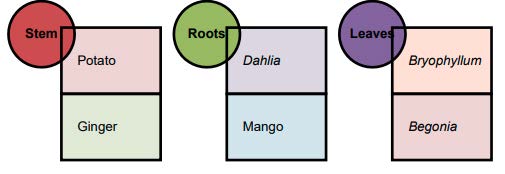
(a) Vegetative Propagation by Stems
The stems (or branches) of plants normally bear buds in the axils which can be used in vegetative propagation to produce new plants. New plants can be obtained from the stem (or branch) of an existing plant by the method of cuttings. A small part of stem (or branch) of a plant which is removed by making a cut with a sharp knife, is called a cutting. While making a cutting, care should be taken to see that there are some buds on it.
The lower end of stem cutting is buried in the moist soil.The upper part of cutting having bud on it is kept above the ground. The cutting planted in soil is watered everyday. After a few days, the cutting develops roots. The bud grows and produces a shoot (branch with leaves)
The plants like rose, champa, grapes, sugarcane, bananas, Bougainvillea can be grown by cuttings method.
Money plant can also be grown by the cuttings method of vegetative propagation. We can grow money plant even in a jar of water by taking a stem cutting (with a node) from an existing money plant.
Advantage of the cuttings method is that by using this method we can produce many new plants from just one plant quickly, without waiting for flowers and seeds.
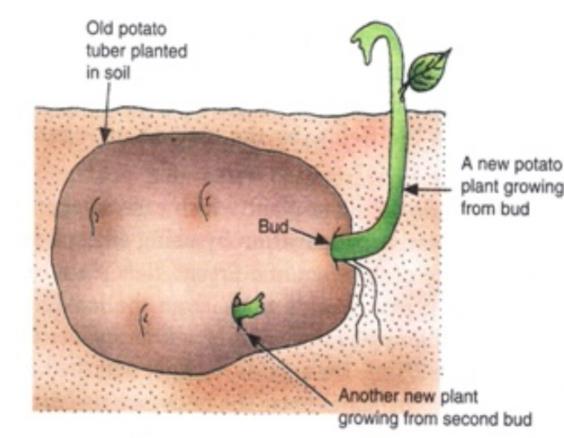
Some of the plants have modified stems which are short and thick, and grow below the ground (or underground). The underground stems have buds from which new plants can be grown. Such underground stems are called stem tubers.
A tuber is the thickened underground stem (or root) of a plant which is swollen with stored food. The tuber has a number of buds. Each bud of the tuber can grow into a new plant when the old tuber (or its cutting) is planted in the soil in the next growing season.Tubers can be used as organs of vegetative propagation to produce new plants.
There are two types of tubers : stem tubers and root tubers.
(a) Potato is a stem tuber
A potato tuber has many buds (called eyes) on its body which appear like scars. When a potato tuber is planted in the soil, then all the buds of potato tuber start growing to produce new potato plants. Thus, one old potato tuber can produce many new potato plants. We can even plant cut pieces of potato in the soil to obtain new potato plants but each such cut piece should have a bud (or eye) on it.
Each potato plant produces more than one tuber, and each tuber has more than one bud (which produce more than one new plant). The vegetative propagation method of producing potato plants by using potato tuber cuttings is much faster than the production of potato plants from seeds.
Ginger and turmeric are also modified, underground stems swollen with food.The underground stems of ginger and turmeric plants have buds on their body.
(b) Vegetative Propagation by Roots
There are some plants which have modified, thickened roots which bear buds.
For example: sweet potato plant has modified roots thickened with stored food which are called root tubers. The root tubers of sweet potato have buds (eyes) on them which can grow to produce new sweet potato plants. Dahlia also has root tubers. The root tubers of Dahlia have buds in them which can grow to produce new Dahlia plants.
(c) Vegetative Propagation by Leaves
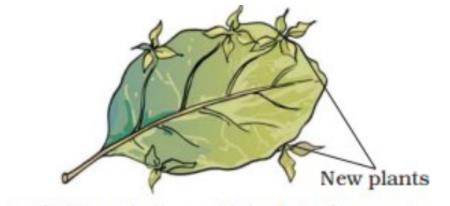
The leaves of some plants develop buds on them. Such leaves having buds can be used as structures of vegetative reproduction in plants.
A plant which can reproduce from its leaves is Bryophyllum (Bryophyllun is also called sprout leaf plant). The leaves of Bryophyllum plant develop some buds in its margins (or edges) When a mature leaf of the Bryophyllum plant falls on the ground, then each bud can grow into a new plant.
Another plant called Begonia also reproduces by vegetative propagation through its leaves. The Begonia plant which can grow into new plants when the leaves fall on the ground.
The plants such as cacti produce new plants when their parts get detached from the main body and fall on the ground (singular of cacti is cactus). Each detached part of a cactus plant which falls on ground can grow into a new plant.
Advantages of Vegetative Propagation Of Plants
- The new plants produced by vegetative Propagation take much less time to grow and bear flowers and fruits as compared to the plants grown from seeds.
- The new plant produced by Vegetative Propagation are exactly like the parent plant .So all the desirable features of the parent plant will be replicated in the new plant.
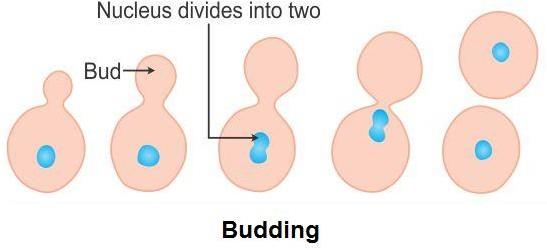
Budding
- In budding, a small part of the parent plant body grows out as a bulb-like projection called the bud, which detaches and becomes a new plant. Example: Yeast.
Fragmentation
- Fragmentation involves breaking up of the plant body into two or more pieces on maturing, each of which subsequently grows to form a new plant. Example: Spirogyra.

Spore Formation
Parent plants produce hundreds of tiny spores in spore cases. When these spore cases burst, spores are spread into the air. Under favourable conditions, the spores germinate and develop into new individuals. Examples: Rhizopus(bread mould), mosses and ferns.

Sexual Reproduction
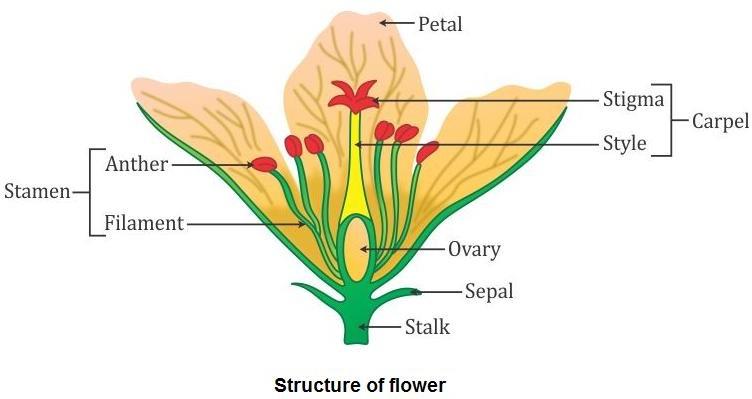
- Flowers are reproductive parts of a plant. The stamen is the male reproductive part, while the pistil is the female reproductive part.
- Flowers with either only stamen or only pistil are known as unisexual flowers. Examples: Corn, papaya and cucumber.
- Flowers which contain both stamen and pistil are called bisexual flowers. Examples: Mustard, rose and Petunia.
- The stamen consists of anther and filament. The anther contains pollen grains which produce male gametes.
- The pistil consists of stigma, style and ovary. The ovary contains one or more ovules. The female gamete or egg is formed in an ovule.
- Male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote.
Pollination
- Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower.
- When pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower, it is termed as self-pollination.
- When the pollen grains of a flower land on the stigma of another flower of the same plant, or that of a different plant of the same kind, it is known as cross-pollination.
- The pollen grains are light and can be easily carried by wind or water.
- Insects help in the transfer of pollen by carrying the pollen on their body on their visit to the flower.
- Pollination in aquatic plants such as Vallisneria and Hydrilla is carried out by water.
Fertilisation
- The fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote is termed as fertilisation.
- Male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into an embryo.
- The embryo is that part of the seed which develops into a new plant.
Fruit and Seed Formation
- After fertilisation, the ovule present in the ovary grows to become a seed and the ovary grows into a fruit.
- The other parts of the flower dry up and fall off.
- The seed contains the embryo enclosed in a protective seed coat.
- Apples, oranges, mangoes, plums, tomatoes, walnuts and almonds are fruits with seeds.
Seed Dispersal
- If all the seeds germinate in the same place, then there would be an unhealthy competition for food and light between plants.
- This is avoided due to dispersal of seeds.
How seeds and fruits are dispersed
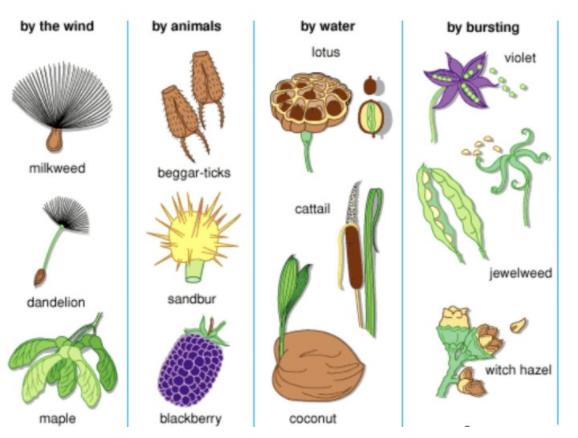
The main agents for the dispersal of seeds and fruits are wind, water and animals.Some seeds are also dispersed by an explosive mechanism in which the ripe fruits of some plants burst on their own by making a little explosion and throw their seeds away from the plant with a great force.The various seeds and fruits have some special features in them due to which they are adapted to be carried away easily by wind, water or animals.
Dispersal of Seeds and Fruits by Wind
The seeds and fruits dispersed by wind either have wing-like structures or they have hair or they are very small and light, which helps them to be easily carried away by the blowing wind.
For example:
- The seeds of drumstick plant have wings so that they can be carried away by wind to far away places and dispersed. Thus, drumstick plant has winged seeds. Similarly, the seeds of maple plant also have wings which help in their dispersal by the wind.
- The seeds of madar (aak) have hair which allow them to be carried away easily by the wind.The fruits of sunflower have hair which enable them to be blown away by wind and get dispersed. So, the sunflower plant has hairy fruits. The cotton plant has also hairy seeds which are easily carried away by wind and dispersed.
- The plants like grass, orchids and Begonia have very small and light seeds which can be easily blown away by the wind for dispersal.
Dispersal of Seeds and Fruits by Water
- The seeds and fruits which are dispersed by water develop floating ability in the form of spongy or fibrous outer coats.
- The seeds of water lily plant and coconut plant are dispersed by water.
- The seeds of water lily plant have a spongy outer coat which allows them to float in water and move to other places along with water currents. The coconut fruits have a fibrous outer coat which enables them to float in water and carried away by flowing water to far off places. It is due to the dispersal of coconut fruits by sea-water that coconut trees grow in all the coastal areas.
Dispersal of Seeds and Fruits by Animals
- Some fruits develop hooks on their surface by which they get attached to the hairy bodies of the passing animals and carried away to distant places.
- These fruits may be carried several kilometres by the moving animals before they are rubbed off from their body and fall to the ground. When the fruits are dispersed by an animal, the seeds present in them are automatically dispersed.
- When the fruits of Xanthium and Urena are dispersed by animals, the seeds of Xanthium and Urena present inside these fruits also get dispersed.
Dispersal of Seeds by an Explosive Mechanism
- When some fruits ripen, strain is set up in their walls until the fruits split into two halves (making a small explosion) and their seeds are thrown away from the plant with a great force in all directions. Thus, some seeds are dispersed when their fruits burst with a sudden jerk.
- The ripe fruits of castor plant burst suddenly with a jerk and scatter the seeds far away from the parent plant. Similarly, the ripe fruits of balsam plant burst suddenly with a jerk and throw their seeds far away from the parent plant. Thus, the two plants whose seeds are dispersed by an explosive mechanism involving the sudden bursting of their ripe fruits are : Castor and Balsam