Electric Current and its Effects
Electric Current
The flow of charges through a circuit is called electric current. The SI unit of electric current is ampere and donated by A. The direction of the electric current is conventionally from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of a cell.
Electric Current and Its Effects:
Electrical energy is the most useful form of energy as it can easily be converted into various other forms of energy such as heat energy, light energy, mechanical energy and chemical energy.
Symbols of Electric Current
- Electric components are represented by symbols.
- Symbols are used in circuit diagrams to show how a circuit is connected.
| Sr. No. | Electric Component | Image | Symbol |
| 1. | Electric Cell |  | |
| 2. | Electric Bulb |  |  |
| 3. | Switch in ‘ON’ Position |  | |
| 4. | Switch in ‘OFF’ Position |  | |
| 5. | Battery |  | |
| 6. | Wire | | |
Electric Circuit
- Electric current that flows through wires, cells, a key, a bulb etc. in a closed path is called an electric circuit.
- It is also known as a closed circuit.
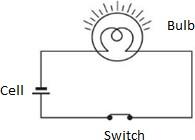
- The bulb glows only when the switch is in the ‘ON’ position.
- A cell has two terminals:
- Positive terminal (+)
- Negative terminal (−)

- A key or a switch used in the circuit usually breaks the circuit when it is in the ‘OFF’ position and allows the electric current to flow when it is in the ‘ON’ position.
Components of an electric circuit
Cell or battery:
- A cell is a source of current.
- It has a positive and a negative terminal.
- When two or more cells are connected such that the positive terminal of one cell touches the negative terminal of the other, it forms a battery, but they have to be connected in a proper manner for electricity to flow through the circuit. They can be connected in series or in parallel.

Switch:
- A switch is used to close or open a circuit.
- When the switch is off, the circuit is open and no current flows through it.
- When the switch is on the circuit is closed allowing current to flow.

Electrical appliance:
- An electrical appliance is a device that uses the current flowing through it to function.
- Electric bulbs, electric iron, fans, electric motors are some commonly used electrical appliances in our daily life.

Wires:
Wires connect the element of the electric circuit. They are made up of materials that are good conductors of electricity such as copper.

Heating Effect of Electric Circuit
- When an electric current is passed through a metallic wire, it gets heated up. This is known as the heating effect of current.
- Electric room heater or an electric heater works on the heating effect of electric current.
- It contains a coil of a wire called an element.
- This element becomes red hot and produces heat. The amount of heat produced in the wire depends on its material, length and thickness.
Electric Fuse
- An electric fuse is an important application of the heating effect of electric current.
- The wires of an electric fuse are made of materials which melt quickly and break when large electric current is passed through them.

- There is a maximum limit on the current which can safely flow through a circuit.
- If the current exceeds this safe limit, then the wires may become overheated and cause fire. Hence, a fuse is used to prevent such a dangerous occurrence.
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- When an electric current passes through a wire, it behaves like a magnet. This is known as the magnetic effect of the electric current.
- When a compass is brought near such a current-carrying conductor/wire, the needle of the compass gets deflected because of the flow of electricity. This shows that electric current produces a magnetic effect.
Electromagnets
- An electromagnet can be defined as a soft-iron core which is magnetized temporarily by passing a current through a coil of wire wound on the core.
- When the electric current is switched off, the coil generally loses its magnetism. Such coils are called electromagnets.
- Electromagnets are widely used in motors, electric bells, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines as well as in industrial lifting electromagnets for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron.
Electric Bell
- An electric bell is a device which produces sound at the push of a button.

- It consists of a coil of wire wound on an iron piece. This coil acts as an electromagnet.
- An iron strip with a hammer at one end is kept close to the electromagnet.
- A contact screw is placed near the iron strip. When the iron strip is in contact with the screw, current flows through the coil. The coil thus, acts as an electromagnet. It then pulls the iron strip.
- In this process, the hammer at the end of the strip strikes the gong of the bell to produce a sound.
- When the electromagnet pulls the iron strip, it breaks the circuit, and the current through the coil stops flowing.
- The iron strip comes back to its original position and touches the contact screw again. This completes the circuit and the current flows in the coil and the hammer strikes the gong again.
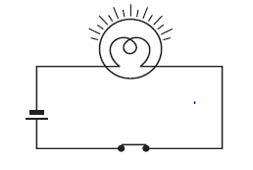
Circuit diagram
A schematic diagram that represents an electric circuit using the standard symbols of the components used in the circuit is called a circuit diagram.
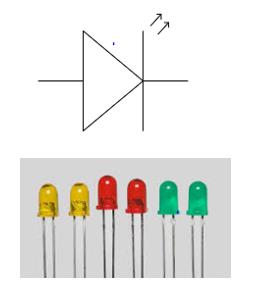
Light emitting diode (LED)
- Nowadays, Light emitting diodes (LEDs) are used instead of an electric bulb because they consume less electricity, do not produce heat, have very long life and are almost unbreakable.
- An LED allows electric current to follow in one direction only.
- LED cannot tolerate even a small change in electric current. A circuit with an LED therefore requires an appropriate resistor. The resistor regulates the flow of electric current and protects the LED.
What makes a bulb glow
- A bulb glows due to the heating effect of electric current.
- A bulb has a partial vacuum, argon gas and a thin filament of tungsten.
- Tungsten metal has a very high resistance and very high melting point.
- When an electric current pass through the filament, due to its high resistance, its heat up quickly to about 2500 degree Celsius.
- At this temperature, the tungsten filament begins to glow and emits light.



