Light
- Light is defined as a radiation which is visible to the human eye.
- The natural source of light on the Earth is the Sun.
- Sunlight plays an important role in the process of photosynthesis and thereby, in the growth of plants.
- Other sources of light are candlelight, fire, lasers, tube lights, electric bulbs etc.
- Light can travel through vacuum, i.e., it does not require a medium to travel.
- The path of light is always straight and not curved. It does not bend.
- Examples: Light emitted from a torch and the headlights of a vehicle.

- The direction of light can only be changed by reflection.
Reflection of Light
- The bouncing of light from a smooth surface such as a mirror is called reflection of light.
- Due to the reflection of light, the impression of an object formed in the mirror is called the image of the object.
- As the distance of the object from the mirror increases, the distance of the image also increases.
- Example: A candle placed in front of a plane mirror appears as if a similar candle is placed behind the mirror.

- An image formed by a plane mirror is erect and of the same size as the object.
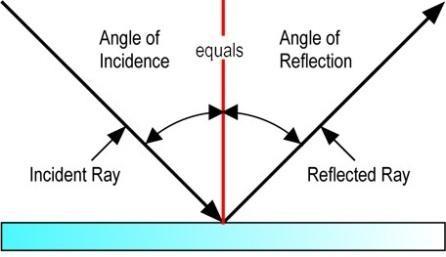
Laws of Reflection
The laws of reflection are:
- The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface, all lie in the same plane.
Types of Reflection
Regular Reflection
- Regular reflection is the reflection of light rays from a smooth surface such as a mirror, glass or water.
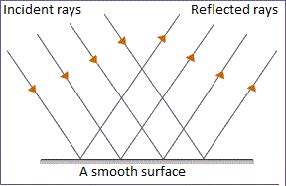
- The reflected rays of light move in a fixed direction.
- Images formed by regular reflection are always clear and distinct.
Irregular Reflection or Diffused Reflection
- Irregular or diffused reflection is the reflection of light from a rough surface such as a plastic sheet, writing paper, wooden board, cloth, skin, leather etc.
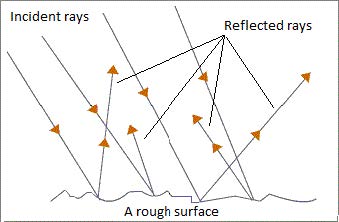
- This reflection occurs when a ray of light is incident on a wall or wood, which is not smooth or polished.
- The reflected rays do not travel in the same direction.
Left-Right Inversed
- It means that the images are inversed, i.e. the right part of an object appears on the left in the formed image, and the left part of the object appears to the right.

- Example: The word ‘AMBULANCE’ is painted left-right inversed. When the driver of a vehicle in front looks into the rear-view mirror, he can read the word AMBULANCE quickly and make way.
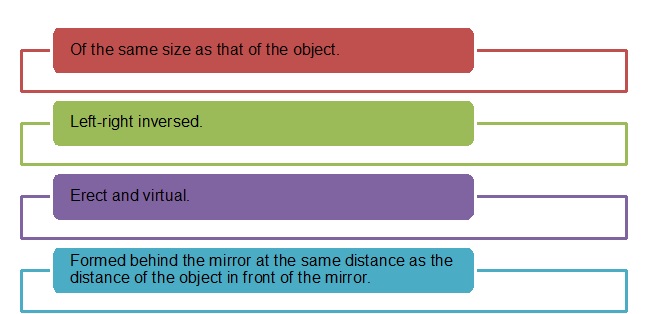
Characteristics of an Image
- The image formed by a plane mirror is:
Spherical Mirrors
- Spherical mirrors have curved reflecting surfaces and are also called curved mirrors.
- These mirrors are made from a hollow sphere.
- There are two types of curved surfaces at each hemisphere:
- Inner curved surface
- Outer curved surface
- The inner curved surface is called concave, while the outer curved surface is called convex.

There are two types of spherical mirrors:
Concave Mirror
- If the reflecting surface of a mirror is concave, i.e. bent inwards, then it is called a concave mirror.

- A concave mirror is used to magnify objects.
Uses of Concave Mirrors
- These mirrors are used by dentists to obtain a magnified image of the teeth.
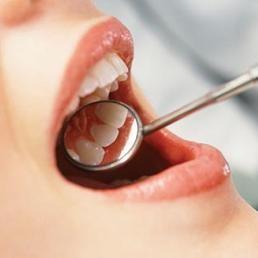
- Doctors use concave mirrors to examine the ears, nose and throat.
- They are used in headlights of cars and scooters in order to increase their focus and brightness..
- People use it to shave and apply makeup.
Convex Mirror
- If the reflecting surface of a mirror is convex, then it is called a convex mirror.

- A convex mirror is also known as a diverging mirror or a fish eye mirror.
- The image formed by a convex mirror is virtual, erect and diminished, which means that a larger area is visible in a convex mirror than in a plane mirror of the same size.
Uses of Convex Mirrors
- These mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors in cars and motorcycles, as they enable the driver/rider to view the road and the vehicles behind.

- They are also used in supermarkets, stores and ATM centres as a security measure.
Types of Images formed by a Mirror
- A mirror forms the following two types of images – Virtual and Real.
Virtual Image
- The image formed by a mirror which cannot be captured on a screen is called a virtual image.
- It is always erect.
Real Image
- The image which can be captured on a screen is known as a real image.
- It is always inverted.
Example: In a camera, images are real and can be captured on the negative, which acts as a screen.
Lenses
Concave Lens
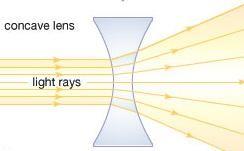
- When light rays are incident on a concave lens, they bend outwards or diverge.
- This lens is also called a diverging lens.
- A concave lens is thinner at its center than at its edges.
- It is used to correct short-sightedness.
Convex Lens
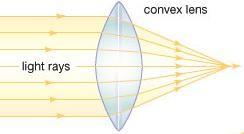
- When light rays pass through a convex lens, they bend inwards and converge at a common point to form an image of the source of light.
- This lens is also called a converging lens.
- A convex lens magnifies the object viewed through it.
- A convex lens is thick in the middle and thin at its edges.
- When the object is placed close to a convex lens, the image formed is virtual, erect and magnified.
- When the object is placed at a far off distance from a convex lens, the image formed is real, inverted and diminished.
Applications of Lenses
- Lenses are used in magnifying glasses, peepholes, cameras, bioscopes, binoculars, telescopes, microscopes and projectors.
- A refracting telescope uses a concave mirror and a convex lens.
Dispersion of Light
- The phenomenon of splitting of a beam of white light into its constituent colours on passing through a prism is called dispersion of light.
- A rainbow is formed when white light from the Sun passes through tiny prism-like water droplets and splits into different colours.
- The order of colours from the lower end is violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red, i.e. VIBGYOR.

