Water: A Precious Resource
- Water is an important natural resource.
- 71% of Earth is covered with water.
- Readily available water for use is only 0.006% of the total water present on the Earth.
- Water exists in three forms: solid, liquid and gaseous.
- Snow and ice are present as ice caps at the poles of the Earth, snow-covered mountains and glaciers are solid form of water.
- Oceans, lakes, rivers and underground water represent liquid form of water.
- Water vapour in air is the gaseous form of water.
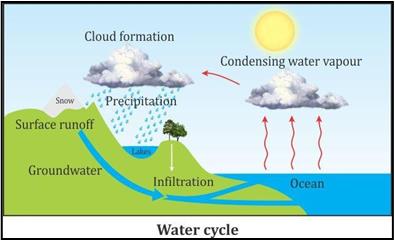
Water Cycle
- Freshwater supply on land has been maintained by the water cycle.
- Physical processes such as evaporation, condensation, precipitation and infiltration occur continuously one after the other and constitute the water cycle.
- The continuous cycling of water among its three forms keeps the total amount of water on the earth constant.
Uses of water
| Body functions | Plants need water to prepare their own food and for germination of seeds. Animals and human beings need water for digestion and absorption of nutrients. |
| Domestic use | We need water for drinking, cleaning, cooking, bathing, washing, etc. |
| Agricultural use | Crops like paddy, wheat, sugarcane, etc. need a large amount of water to grow. |
| Industrial use | Water from river is used to produce electricity. |
| Use in transport | Huge ships transport goods containers and people all around the world through rivers, seas and oceans. |
| As a habitat | Different freshwater and marine water bodies are the habitat for different kinds of plants, animals, fish and microorganisms. |
Sources of water:
- Rain is one of the main sources of freshwater. Some of the rainwater that falls on the land surface may flow into rivers, streams or oceans. This is called runoff water. The runoff water either flows into rivers or gets stored in lakes to form a freshwater source.
- Surface water: After rainfall, water gets collected in the low- lying areas to form ponds and lakes. In hilly regions, the runoff water falls from higher areas to form rivers that flows into valleys. The rivers further flow two seas or oceans. All these water sources form the surface water of the earth.
- Underground water: During the summer season or in case of failure of rainfall, people depends on the water from underground sources for domestic and agricultural purposes.
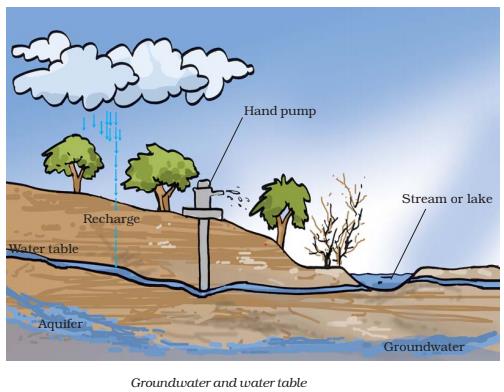
- Rain water gets collected in the soil by seeping into the gravel and rocks at the bottom. The excess amount of water moves deeper into the ground and fills the spaces in the rocks. This is known as groundwater. The level of groundwater is known as the water table.
- Aquifer: The rainwater that has collected in the empty space in the porous layer of rock is known as an aquifer. The water remain there because below it is a hard layer of rock which prevents water from moving further downwards.
Groundwater and Depletion of Water Table
- On digging the ground near a water body, a level is reached where all the space between the particles of soil and gaps between the rocks are filled with water. The upper limit of this layer is termed water table which varies from place to place.
- The water found below the water table is called groundwater.
- The process of infiltration helps in replenishment of groundwater.
- An aquifer is a place where groundwater is stored between layers of permeable rock below the water table. By using hand pumps or tube wells, water in aquifers can be pumped out.
- Increase in the usage of water may be due to a rise in population and industrial and agricultural activities.
- Scanty rainfall, deforestation and decrease in the effective area for seepage of rainwater are other reasons for depletion of water.
- Some places receive good amount of rainfall, while regions such as deserts have scanty rainfall. For example, in India, Assam receives an average annual rainfall of 280 cm, whereas Rajasthan receives an average annual rainfall of only about 49 cm.
- Excessive rains may cause floods, whereas insufficient rains may cause droughts.
Water Management
- Leakage in pipes leads to wastage of water.
- People often leave the taps open while shaving, bathing, brushing and washing vegetables even when not required.
- Most rainwater flows into water drains and becomes useless. Such wastage of a precious natural resource must be stopped.
Proper Management of Water
| Percolation Pit | An important technique is rainwater harvesting which involves construction of percolation pits and recharge wells to recharge groundwater. |
| Bawri | A traditional way of collecting water is the ‘bawri. It was primarily constructed for collecting water to be used during times of drought. |
| Drip Irrigation | Drip irrigation is another technique of watering plants by making use of narrow tubes which deliver water directly at the base of the plant. It minimises the use of water in agriculture. |
Water – Wise Habits

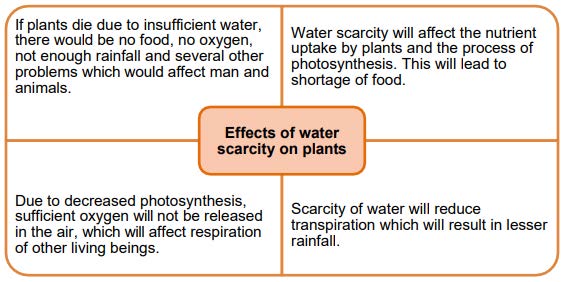
Effects of Water Scarcity on Plants
Methods of Conservation of Water
Economic use and conservation of water are the two main methods to save water.
- Rainwater harvesting: A lot of rain water goes into storm drains during the rainy season. This water can be conserved for use or to replenish the groundwater levels by the method of rainwater harvesting. Rainwater harvesting can be done by collecting rainwater from rooftops and storing it in tanks. The water can be used for various household purposes. Rainwater harvesting can raise the underground water table of the region.
- Check dams: Rainwater percolates into the soil only if it does not flow away quickly. Water can be prevented from flowing away by constructing check dams in the path of its flow.
- Drip irrigation: The drip irrigation system supplies the required amount of water only around the roots. Since water is supplied drop by drop, water loss through evaporation and runoff is prevented thus saving water.
- A huge amount of potable water is lost during the distribution of water because of leakage in the main water pipelines. Fixing these leakage can save a lot of water from going into the drains.
- Care should be taken by not to pollute the lakes and ponds by using them for washing clothes, bathing animals and other human activities.
- Another simple and effective method to reduce the usage of water is by recycling the water from industries and using it for horticulture purposes.
Distribution of water in India
- The movement of wind influences rainfall in India. Rainfall varies from place to place and the distribution of water is uneven.
- Some regions such as those of Rajasthan, Northern Karnataka and Gujarat do not have sufficient rainfall and are prone to drought, whereas some regions such as Andhra Pradesh, Orissa, West Bengal receive excess rain causing floods.
- Dams are built to maintain and distribute water supply. Artificial walls are built across the river that control the flow of water in them. It holds a reservoir whose water content is maintained by the opening and closing of the gates.
- The Bhakra-Nangal dam is built on the river Satluj and provides water to the states of Punjab and Haryana.