Forests: Our Lifeline
- A forest is an area with a high density of trees. Today, forests occupy approximately one- third of the Earth’s land area. Forests are home to many animals and plant species.
There are three major types of forests- tropical, temperate and boreal forests.
Forest profile
There are different kinds of plants of varied height and size in the forests. Parts of a tree above the stem, including the branches and leaves are collectively known as the Crown. Trees belonging to the genus Pinus have tapered crowns, while a neem tree has a Crown that looks like a globe.
Components of a Forest
- Living components: Plants, animals and microbes.
- Non-living components: Soil, air and water.
Structure of Forest

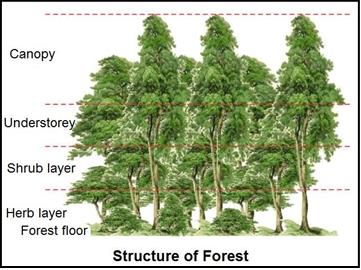
- The branchy part of a tree above the stem is known as the crown of the tree.
- Crowns are mainly responsible for the absorption of Sun’s light energy, performing photosynthesis, releasing oxygen and carrying out processes such as respiration and transpiration.
Forest Floor
- This is the ground layer of a forest.
- The soil is moist and water containing decaying leaves, fruits and animal matter.
- This layer of forests is home to rabbits, snakes, frigs, earthworms, fungi termite and insects.
- The decomposers (microorganisms) present on the forest floor decompose the dead plant and animal matter to form fertile soil known as humus.

Interdependence of plants and animals in a forest
- The plants and animals in a forest depend on each other for their survival. Plants are autotrophs, so also called producers.
- Living things that eat other organisms as food are called heterotrophs. All animals are heterotrophs, so also called consumers.
- Some animals eat only plants, such animals are called herbivores.
- Carnivore’s animals eat only other animals, whereas omnivorous animals eat both plants and animals.
- When animals die, their bodies are eaten by crows, vultures and hyenas. This group of animals is called scavengers.
- The bodies of dead plants and animals get broken down into simpler substances or are decomposed by decomposers like fungi and bacteria present in the soil. The fertility of soil is increased by these decomposers.
- The energy from the plants enters the consumers in the form of food. This eventually ends up at the decomposers and is released into the soil. This is again used by the plants forming a cycle known as the cycle of nutrients.
Dependence of plants on animals:
- Not only do animals depend on plants, but plants also depend on animals in many ways.
- Insects and birds feed on the nectar found in the flowers of plants. This helps in the process of pollination of flowers, which leads to the reproduction of plants.
- Fruits and seeds, which are produced after pollination, are dispersed by the animals in different places.
Forest- An Ecosystem
- An ecosystem is a self-sufficient unit of the living and non-living environment only requiring energy from the sunlight for its functioning.
- Living beings not only interact with each other but also with the non-living components of the forest.
- Plants interact with soil to obtain nutrients, with water to prepare food during photosynthesis and with
- air to obtain carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
- Living beings interact with one another through the food chain. Example: Grass is eaten by a grasshopper; the grasshopper is eaten by a frog; the frog is eaten by a snake; and the snake may be eaten by a hawk.

- If any one of the components of a food chain is destroyed, it will disrupt the food chain causing imbalance in nature.
- All the food chains interlink to form a food web.
- When plants and animals die, decomposers decompose their bodies into nutrients, water and carbon dioxide.
- In this way, water and nutrients are returned to the soil and carbon dioxide is returned to the air. These are reused and the process goes on like a never-ending chain.
Importance of Forests

Regeneration of Forests
- The trees and plants in a forest can grow and regenerate on their own.
- The organisms decompose the wastes and the dead bodies of plants and animals and convert them into humus which mixes with the soil making it fertile and appropriate for plant growth.
- In addition, animals and birds help in seed dispersal which helps in the growth of plants in different areas of the forest.
Conservation of Forests
Benefits of Forests
Purification of Air:
Photosynthesis takes place in all kinds of plants, trees and algae in a forest, which releases oxygen that is used by plants and animals for breathing. Animals breathe out carbon dioxide which is used by plants during photosynthesis. So, a balance is formed between the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air.
Plants and trees in a forest removed excess water through the stomata present on the underside of the leaves. This process is called transpiration, which helps in the water cycle and keeps the atmosphere cool.
Rainfall Due to Forest:
Rainfall is dependent on forests. Excess water from the trees is released in the form of water vapour by the process of transpiration and helps in the formation of Clouds by a process of condensation, which undergoes precipitation to form rain. The absence of forests and trees may lead to floods, soil erosion, depletion in the water table and poor rainfall.
Prevention of Soil Erosion:
Soil erosion is the removal of the top layer of soil. The roots of the trees hold the soil together and help the water to infiltrate into the soil. In this way, soil erosion due to the runoff water and wind is prevented by the forests. Hence, trees act as windbreakers.
Forests- A Source of Wood:
A well-managed forest is a rich source of timber wood and bamboo, which is used for construction houses, making furniture, and building ships. Trees such as teak, shisham, rosewood, oak, willow, and sandalwood are sources of wood.
Forests- A Source of Medicinal Plants and Edible Fruits:
A forest is a storehouse of a variety of medicinal plants, some of which do not grow anywhere else. Quinine, a medicine used to treat Malaria is extracted from the bark of the cinchona tree. All parts of the ‘trumpet tree’ are used to treat respiratory illness while lemongrass is used to treat fever, colds and coughs.
Forests- A Storehouse of Biodiversity:
The variety of living organisms found in a region form the biodiversity of the region. A Forest is a huge storehouse of biodiversity. Some plants and animals are found only in certain forest regions of the world. For example, the golden lion tamarins are found only in some forests of Brazil etc.
Destruction of Forests
Deforestation is the destruction of large number of trees in a forest and overuse of forest resources. The following are the reasons for deforestation:
- Construction of dams, highways and clearing of forest to convert them into cultivable land and other residential areas.
- The need for timber and medicinal plants, resulting in illegal logging and smuggling of the precious forest products.
- Construction of resorts in and around forests, leading to their destruction.
- Lack of awareness in people about the importance of forests.
- Overgrazing in forest by cattle from nearby villages.
- Poaching and hunting of animals for their meat, skin and bones causing a decrease in the number of animals and disturbance in the food chain.


