Soil
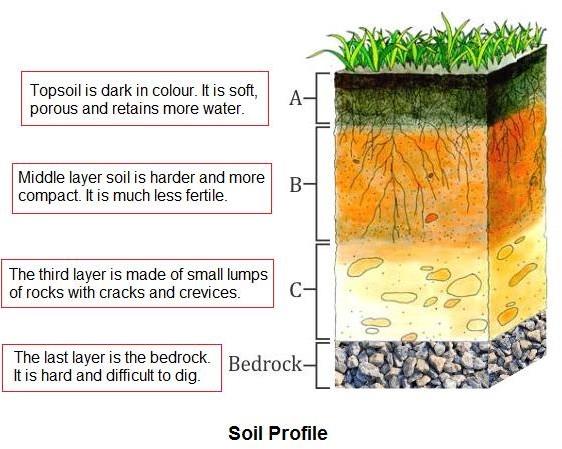
Soil Profile
- Soil is a mixture of decomposed rock and mineral material with decayed organic matter called humus.
- A process termed weathering results in the formation of soil. Weathering is the disintegration and decomposition of rocks and minerals over a period of time.
- The nature of the soil depends on the rocks from which it has been formed and the type of vegetation which grows on it.
- A soil profile is a vertical section through different layers or horizons of the soil. Each layer has different texture, colour and chemical composition.
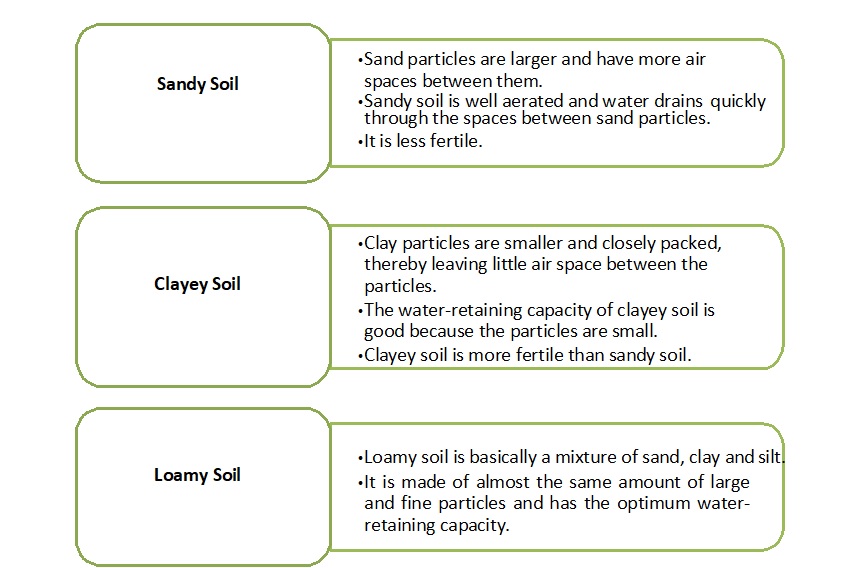
Types of Soil
Properties of Soil
- Soil contains air and moisture.
- Soil allows water to percolate. Percolation is the process by which water passes down slowly through the soil.
Soil and Crops
- Soil profile is affected by climatic factors such as wind, rainfall, temperature, light and humidity which bring about changes in the soil structure.
- The type of vegetation in a particular area depends on the type of soil available in that region.
| Type of soil | Crops grown |
| Clayey and loamy soil | They are suitable for growing cereals such as wheat and gram due to good water-retaining capacity. |
| Loamy soil | It is suitable for growing lentils and other pulses as this soil drains water easily which is good for the crops. |
| Sandy soil or loamy soil | Either of them is suitable for cotton because each drains water easily and holds plenty of air. |
| Clayey soil | It is suitable for growing crops such as wheat because it is rich in humus and is very fertile. |
Soil Erosion
- The removal of fertile topsoil by wind or water is called soil erosion. As a result, infertile sub-soil is exposed which does not support plant growth.
- Deforestation is the primary cause of soil erosion. When trees are absent, there are no roots to bind the soil particles, and hence, rainwater or wind carries away this loose soil causing soil erosion.
- Soil erosion removes the fertile topsoil leaving the land infertile. The land can no longer support agriculture. Soil erosion even causes floods.
- Soil erosion can be prevented by afforestation, which is large-scale growing of forest trees instead of cutting them.
- A piece of land should not be left barren for a long period; the soil should be put to use by regular farming.
Effects of Soil Erosion
The important effects of soil erosion are as follows:
- Soil erosion can turn lush green forests into deserts and spoil the environment: When the fertile top-soil in a forest gets removed by soil erosion, then the infertile sub-soil is left behind. No forest plants can grow in this remaining infertile soil due to which the once lush green forest can gradually turn into a desert.
- Soil erosion can lead to famines (excessive scarcity of food): When the fertile top-soil is removed by soil erosion, then the food crops do not grow well in the remaining infertile soil. And due to bad crops, there is an excessive shortage of food-grains in that area.
- Soil erosion can cause floods: The soil carried away from land by the flowing rainwater gradually deposits on river beds (decreasing their depth). So. when it rains heavily, the river cannot take away all the rainwater quickly Due to this, river water overflows from its banks and causes severe floods by submerging surrounding areas.
Prevention of Soil Erosion
Soil erosion can be prevented in the following ways:
- Soil erosion can be prevented by preventing large scale cutting down of forest trees. The large scale cutting down of forest trees is called deforestation. So soil erosion can be prevented by deforestation.
- Soil erosion can be prevented by afforestation (large scale growing of forest trees in place of cut down trees).New trees should be planted in place of the cut down trees. And this tree cover will prevent soil erosion of the forest land.
- Soil erosion can be prevented by increasing the green cover (vegetation) around us by planting more trees and plants ourselves.
Soil pollution
The contamination of soil with waste materials (especially used polythene bags and plastics), pesticides, fertilisers, acid rain and industrial chemical wastes, etc., is called soil pollution.
The various sources of soil pollution and their effects are as follows:
- Dumping of waste materials (such as polythene bags plastics, glass and metal objects) causes soil pollution. Some waste materials (like paper and vegetable wastes) rot after some time and become harmless. But the waste materials such as polythene bags and other plastics (plastic bottles, etc.) do not rot on their own and remain as such indefinitely. They also kill the living organisms.The used glass and metal objects also do not rot in nature and cause soil pollution.
- The use of pesticides in agriculture causes soil pollution: Pesticides are the poisonous chemical substances which are sprayed on standing crops to save them from the harmful insects and diseases. So, the grains, fruits and vegetables grown in this polluted soil contain pesticides. When we eat such contaminated grains, fruits or vegetables, the pesticides present in them enter our bodies and damage our health in the long run.
- The excessive use of fertilisers in agriculture causes soil pollution: Chemical fertilisers are added to soil in the fields to increase food production. The excessive use of chemical fertilisers makes the soil acidic or alkaline. When the soil becomes highly acidic or alkaline it is said to be polluted.This soil becomes unfit for the growth of crop plants.
- Acid rain causes soil pollution: Acid rain makes the soil highly acidic. This acidic soil becomes toxic or poisonous) for plant growth. In this way, pollution caused by acid rain makes the soil less fertile.
- Dumping of industrial wastes causes soil pollution: Many industries (or factories) dump their waste products containing harmful chemicals on soil. These chemicals cause soil pollution and harm plants which grow in it and the cattle which graze on it.
Prevention of Soil Pollution
The soil pollution can be prevented in the following ways :
- The use of polythene bags should be avoided to prevent soil pollution. This can be done by using bags made of paper, cloth or jute.
- Plastic objects should be sent to factories for recycling to prevent soil pollution. Discarded glass and metal objects can. also be recycled.
- The use of pesticides in agriculture should be minimised to reduce soil pollution.
- The use of excessive chemical fertilisers should be avoided in agriculture to prevent soil pollution.
- Steps should be taken to reduce the emission of acidic gases like sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides from factories which cause acid rain.
- The industrial chemical wastes should be treated properly to make them harmless before dumping into soil.
Important facts on soil
- Land covers 20% of the earth’s surface.
- Top most layer of earth’s crust is called Top soil. It is a mixture of mineral (soil) particles and
- humus.
- Soil particles are formed from rocks and the chemical composition of soil particles depends on the rock from which it is formed.
- Top soil is important for biological activity as it holds roots of all plants and contains different. types of animals and micro-organisms.
- Loss of top soil is called soil erosion and it occurs due to natural and man – made causes.
- Floods and winds are the natural causes for soil erosion. Deforestation, overgrazing and improper tilling are man – made causes for soil erosion.
- Soil erosion is prevented by proper land management, preventing overgrazing, deforestation and Jhoom type farming and by restoring of forest and grass cover.
- Soil is another natural resource, which is rather most precious of all resources, as it is essential for our survival as well as all other life forms.
It provides
- food and fodder
- clothing
- provides anchorage to the plants
- water and minerals to the plants, and water for various human needs, irrigation and industry
- Home to a number of soil organisms.